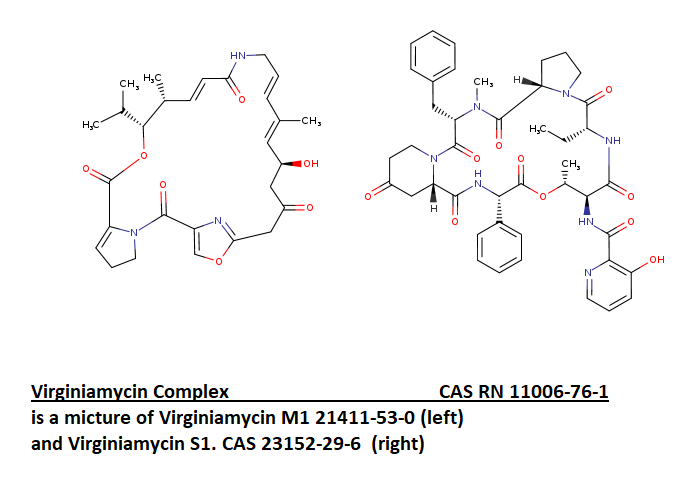
Virginiamycin mixture
Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
Synonyms:
- Mikamycin (7CI)
- Streptogramin (6CI)
- Eskalin 500
- Eskalin V
- Lactrol
- Lactrol XP
- Livelong
- Pyostacin
- Pyostacine
- Stafac
- Stapyocine
- Virgimycin
- Virginiamycin
- Virginiamycin complex
Chemical names:
IUPAC:
RTECS#
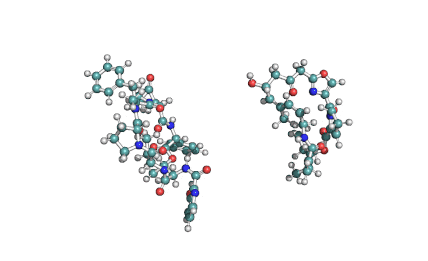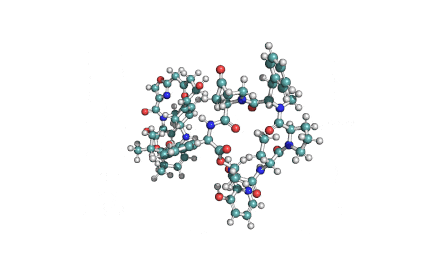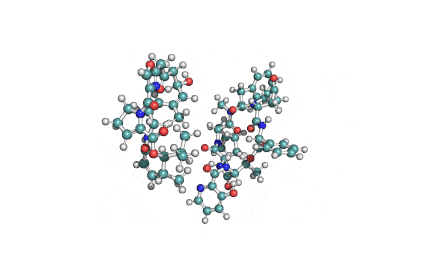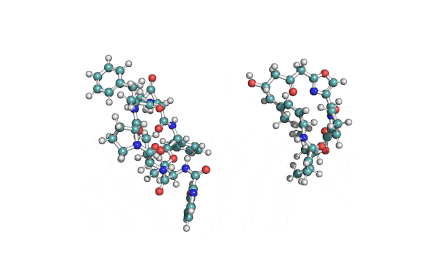
Virginiamycin is a streptogramin. It is a combination of pristinamycin IIA and virginiamycin S1.
Virginiamycin is a streptogramin antibiotic similar to pristinamycin and quinupristin/dalfopristin. It is a combination of pristinamycin IIA and virginiamycin S1. (after Drugbank).
It is used in bio-fuel industry and as cattle growth promoter.
Further Information
- Virginiamycin is used in the fuel ethanol industry to prevent microbial contamination and in livestock to prevent and treat infections. (Drugbank)
- According to a USDA study, antibiotics can save as much as 30% in feed costs among young swine. (Drugbank)
Composition
Supply related information
Special Info
Other Fields