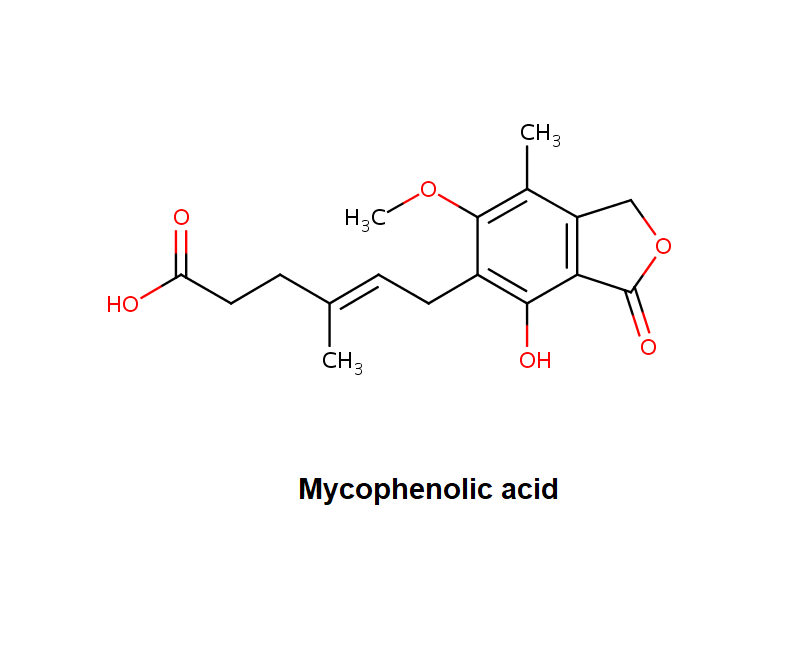
Mycophenolic acid
Details
Specifications
Chemical identification
fatty acid antibiotic
Further Information
DMSO, Ethanol, Methanol, Dichloromethane. Insoluble in water
Immunosupressor
Purine nucleotide synthesis inhibitor
Composition
Other Fields


Immunomodulators are bio-active agents, which suppress, weaken or alter the activity of the immune system. This may consequently weaken inflammatory responses. Immunomodulators (immunosuppreessors) are most often used in organ transplantation to prevent rejection of an implant.
Autoimmune diseases are situations, where the immune system attacks one's own cells, tissues and organs, erroneously recognizing them as alien factors.
Immunomodulators may be used to cure autoimmune deseases.
fatty acid antibiotic
DMSO, Ethanol, Methanol, Dichloromethane. Insoluble in water
Immunosupressor
Purine nucleotide synthesis inhibitor




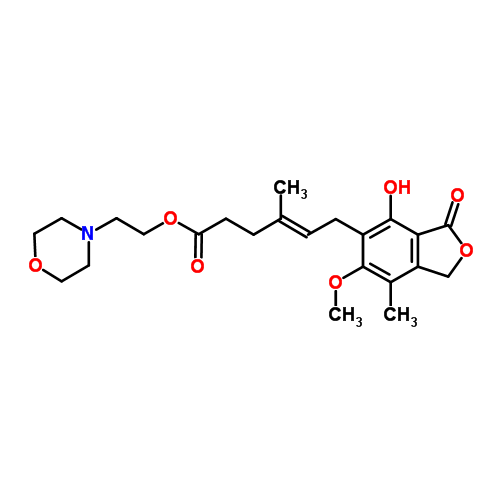
2-Morpholinoethyl (E)-6-(4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-phthalanyl)-4-methyl-4-hexenoate systematic name: 4-Hexenoic acid, 6-(1,3-dihydro-4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranyl)-4-methyl-, 2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl ester, (E)-
RTECS No : MP7746700
Morpholinoethyl ester of Mycophenolic acid
Acetone: freely soluble.Methanol: solubleEthanol: Sparingly solubleNeutral water: about 40 µg/mLWater acidified to pH 4: about 4 mg/ml
Immunomodulator, Immunosuppressor


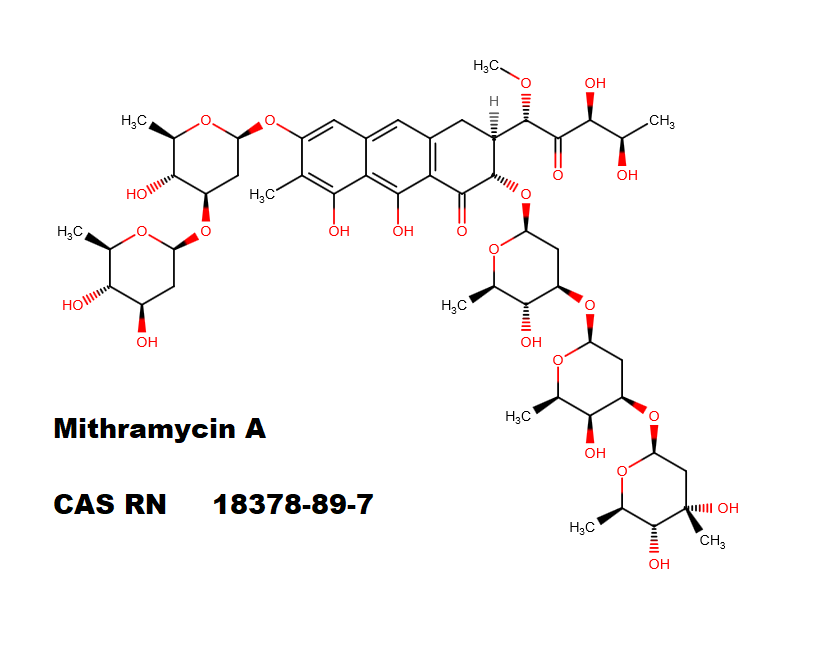
Oligosaccharide antibiotic, a RNA synthesis inhibitor.
DMSO, Methanol, Ethanol
Anthracycline Pentaglycosidic antibiotic.
RNA synthesis inhibitor
DNA binding fluorescent dye. Until 2000 it was used to reduce high levels of plasma calcium. Used as an antineoplastic agent in the treatment of testicular cancer, Paget's disease of bone, and, rarely, the management of hypercalcemia.


RTECS NO0650000
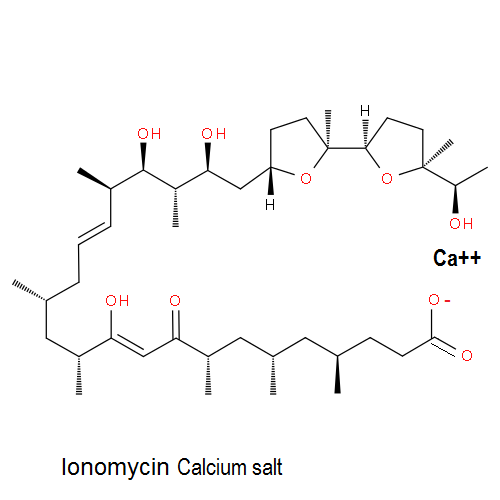
Ionomycin : a potent and selective Ca++ ionophore
DMSO, Ethanol, Methanol
Ionomycin is more effective than A23187 as a Ca++ionophore. Ionomycin is used in research on Ca++ transport across biological membranes; Ionomycin induces apoptotic degeneration of embryonic cortical neurons.


Natural antidepressant. Anti-retroviral agent. A protein kinaze-C inhibitor.
Soluble in alkaline aqueous solutions. Soluble in organic bases such as pyridine (red fluorescent solutions) but not in other organic solvents
Antidepressant. Apoptosis inducer. PKC inhibitor. Antiviral
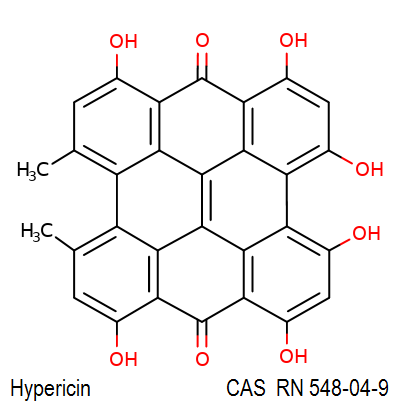


Synonyms
RTECS KB4725000
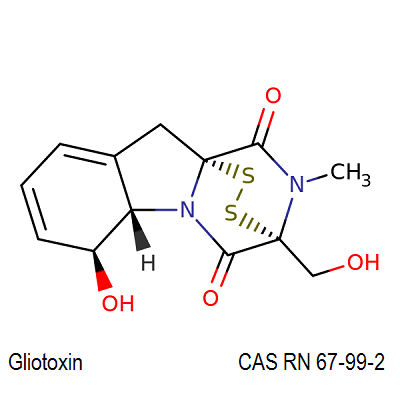
Gliotoxin is a fungal antibiotic mycotoxin with antiphagycytic and immunomodulatory activities.
Gliotoxin is an antibiotic that is toxic to higher animals as well as to animal and plant pathogens and that is produced by various fungi (as of the genera Gliocladium, Aspergillus, andPenicillium)
DMSO, Methanol, Ethanol, Ethyl acetate, Petrol-ether, Dichloromethane. Water insoluble
Chemical class:
Bioactivity class:
Gliotoxin blocks the thiol groups in the membranes . Gliotoxin induces apoptotsis in macrophages and thymocytes. Gliotoxin induces Ca2+ release from intact rat liver mitochondria.


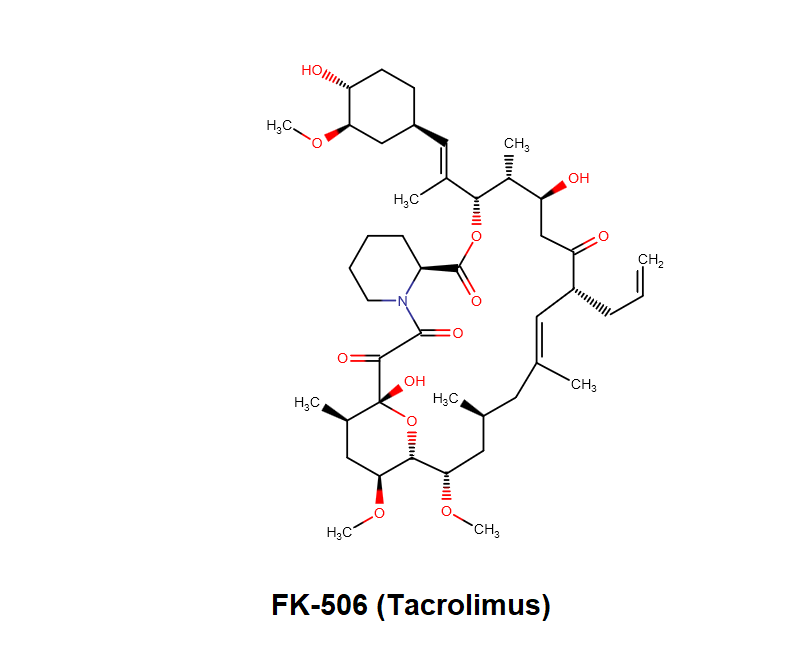
Synonyms: FK506, Tacrolimus,
RTECS: KD4200000
FK506 is 23-membered macrolide lactone discovered in 1984, by Kino T, Hatanaka H and Hashimoto M. [reference 2] FK506 exhibits potent inhibitory effect on T- lymphocyte activation. It binds to immunophilins FK506 binding proteins (FKBP-12) and a complex of FKBP-12, calcium, calmodulin and calcineurin is formed, inhibiting phosphatase activity of calcineurin. This prevents dephosphorylation and translocation of nuclear factor of activated T – cells (NF-AT) and inhibits transcription of early T-cell activation gene, Interleukin-2, Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF-a) and proto-oncogenes; suppressing expression of IL-2 and IL-7 receptor. This results in inhibition of T-lymphocyte activation. FK506 also inhibits the mixed lymphocyte reaction, generation of cytotoxic T-cells and T-cell dependent B-cell activation.
FK506 is soluble in Methanol, Ethanol, Acetone, Ethyl Acetate, Diethyl ether, Chloroform, Dicloromethane. FK506 is sparingly soluble in Hexane, Petroleum ether. FK506 is insoluble in water
Chemical classification:
Macrolide
Bioactivity classification
Immunosuppressant
FK506 (Tacrolimus) is used as an immunosuppressant at organ transplantations. For experimental uses of FK506 (Tacrolimus) read also United States Patent Application 20090098200


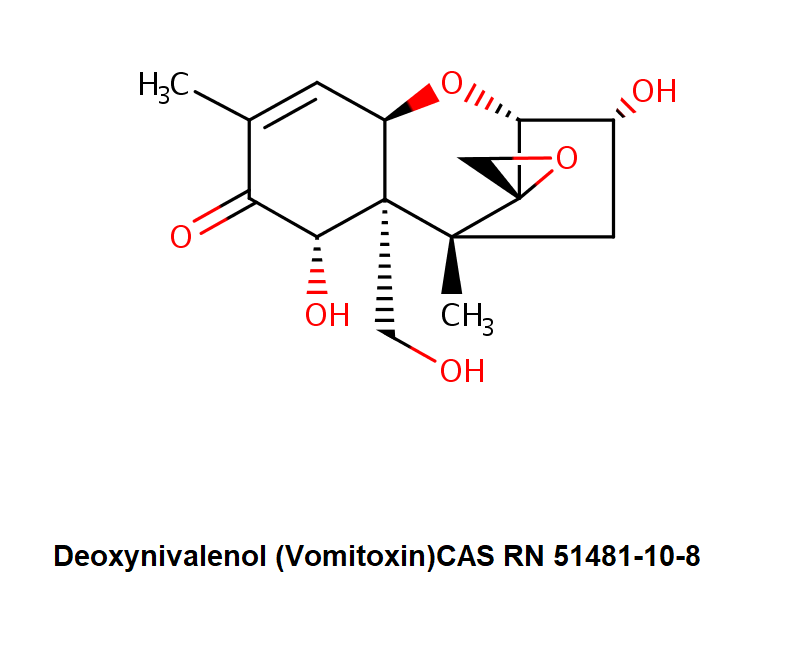
Deoxynivalenol (DON , Vomitoxin) is a type B trichothecene. It occurs in grains such as wheat, barley, oats, rye, and maize, rice, sorghum. Deoxynivalenol (DON) is produced by numerous strains of Fusarium and some other fungi. Deoxynivalenol (DON) poisonings occur both in humans and farm animals. Deoxynivalenol (DON) is highly toxic, producing a wide range of immunological disturbances and is particularly noted for inducing feed refusal and emesis in pigs, hence the alternative name vomitoxin Deoxynivalenol (DON) usually co-occurs with other Fusarium toxins, such as Zearalenone, Nivalenol and its derivates, as well as the group of fumonisins.
Deoxynivalenol (DON ) is soluble in common polar organic solvents as acetonitrile, methanol and ethyl acetate, slightly soluble in water.
trichothecene type B mycotoxin
The main toxic effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) is inhibition of protein synthesis via binding to the ribosome.In agricultural R&D, DON is widely used to select crops strains with increased resistance against Fusarium.


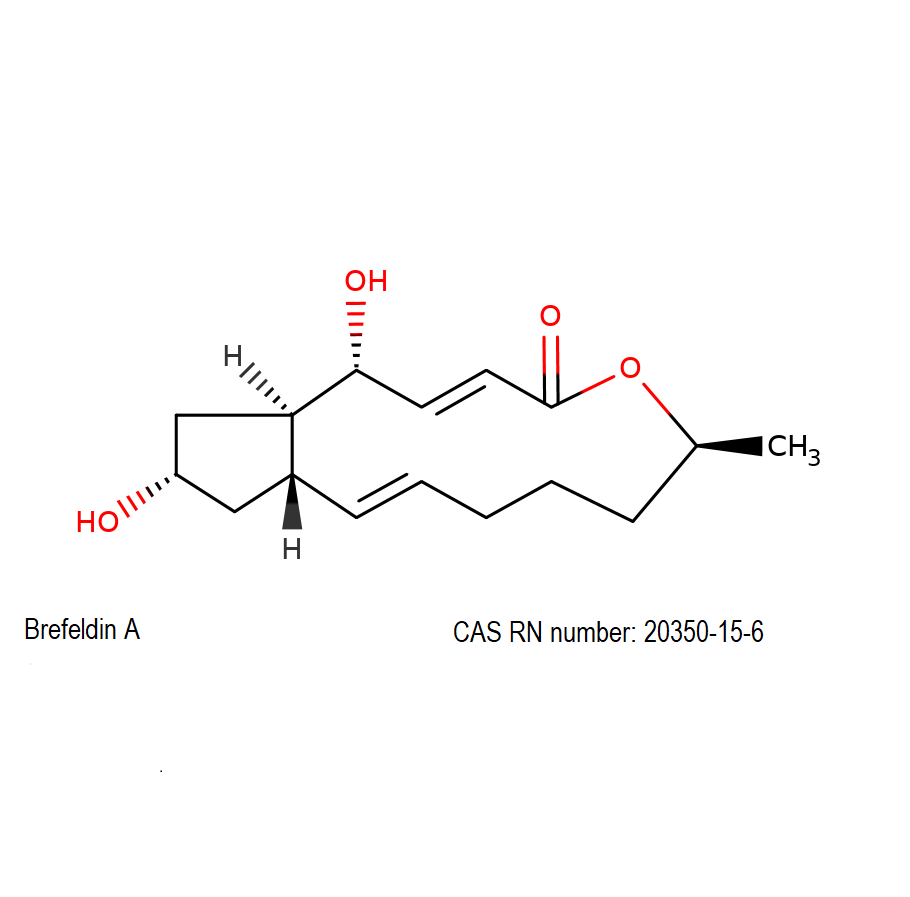
Synonyms:
EC# : 606-528-3
Systematic name:
(1R,2E,6S,10E,11aS,13S,14aR)-1,13-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-1,6,7,8,9,11a,12,13,14,14a-decahydro-4H-cyclopenta[f]oxacyclotridecin-4-one
RTECS: GY8410000
Brefeldin A is a macrocyclic lactone from fungal source, exhibiting a wide range of antibiotic activity.
Methanol, Ethanol, Dichloromethane, DMSO, acetone or ethyl acetate
Inhibitor of protein translocation from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus.
Inhibitor of intracellular protein transport and protein secretionA macrolide isolated from Penicillium brefeldianum. It affects the vesticular transport of the Golgi apparatus and induces DNA fragmentation which leads to apoptosis.
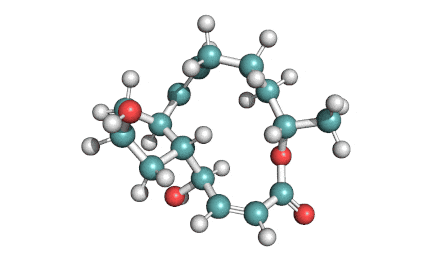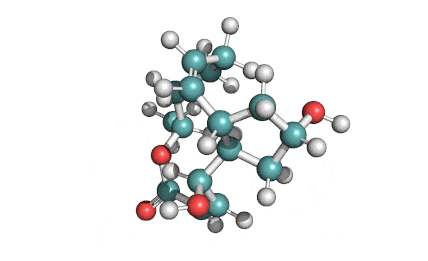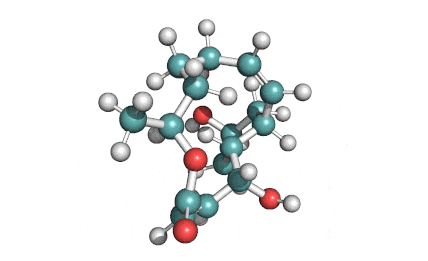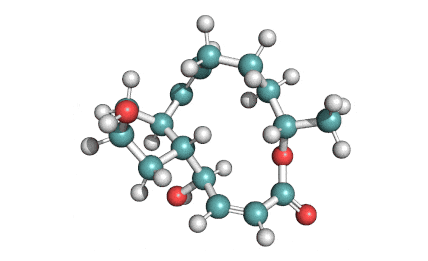


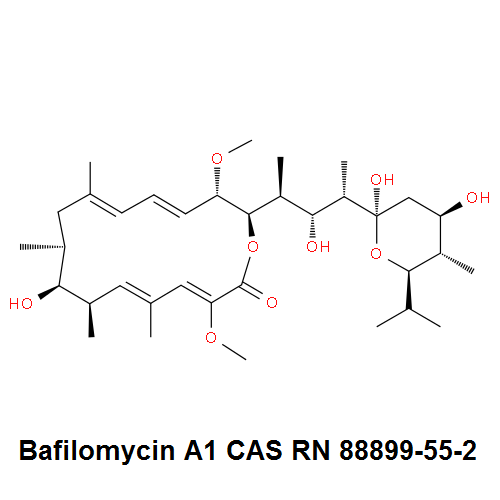
IUPAC Name: (3Z,5E,7R,8S,9S,11E,13E,15S,16R)-8-Hydroxy-16-[(1S,2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-3-[(2R,4R,5S,6R)-tetrahydro-2,4-dihydroxy-5-methyl-6-(1-methylethyl)-2H-pyran-2-yl]butyl]-3,15-dimethoxy-5,7,9,11-tetramethyloxacyclohexadeca-3,5,11,13-tetraen-2-one
Bafilomycin A1 is toxic macrolide antibiotic acts as a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase. It acts as autophagy Inhibitor
Soluble in 100% ethanol, methanol or DMSO.
Macrolide antibiotic
Bafilomycin A1 is a specific inhibitor of vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) in animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms. Bafilomycin A1 is useful in distinguishing among different types of ATPases. Bafilomycin A1 can prevent the re-acidification of synaptic vesicles once they have undergone exocytosis. Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antineoplastic, Immunosuppressive Bafilomycin A1 has been shown to decrease multi-drug resistance.
Bafilomycin A1, inhibits vacuolar-ATPase.
It is a potassium ionophore that impairs mitochondrial functions.
It activates respiration of neuronal cells via uncoupling associated with flickering depolarization of mitochondria.
Bafilomycin A1 has been commonly used as a method of inhibition of infection by viruses known or suspected to follow the path of receptor-mediated endocytosis and low-pH-mediated membrane fusion
Vacuolar ATPase inhibitors overcome Bcl-xL-mediated chemoresistance through restoration of a caspase-independent apoptotic pathway.