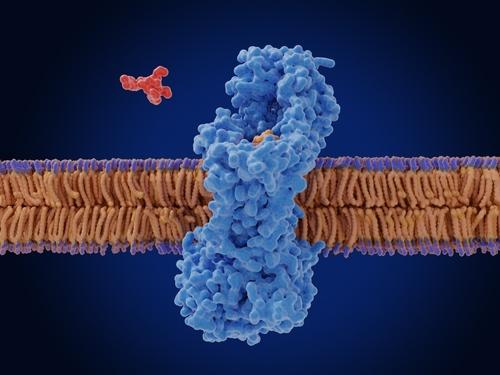
Puromycin is an amino nucleoside antibiotic obtained from the bacterium Streptomyces alboniger. It inhibits protein synthesis by interrupting peptidyl transfer on both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes thereby causing premature chain termination of peptides during translation in ribosomes.
This antibiotic inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and many animal and insect cells. Puromycin is weakly active against Gram-negative microorganisms. It has antimicrobial, antitrypanosomal, and anti-infective, antitumor, antineoplastic properties. Puromycin is most commonly known as a selection marker for cell lines genetically engineered to express a resistance transgene and can also be used in some particular conditions for the selection of E. coli transformants.
Puromycin has a fast mode of action, causing rapid cell death at low antibiotic concentrations. The recommended dose as a selection agent in mammalian cell cultures is within a range of 1-10 μg/ml. According to the Register of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances (RTECS), LD50 value in rats is 20 mg/kg (oral), 25 mg/kg (intraperitoneal), and 15 mg/kg (intravenous). It has been shown that injections of this antibiotic result in both short-term and single-term memory loss in mice. Puromycin is soluble in water as a colorless solution and stable for one year as a solution when stored at -20°C.
Fermentek's Puromycin Products
Fermentek, a leading company in the biotechnology field, focuses on the production of pure biologically active products isolated from nonpathogenic microorganisms (actinomycetes, Nocardia and Streptomycetes) and Fungi (Penicillium, Aspergillus, Fusarium).
Fermentek offers pure Puromycin dihydrochloride, Puromycin amino nucleoside and Puromycin dihydrochloride animal free, which can be used for cell biology research, enzymatic embolic studies, hormonal system studies as well as a selection in vitro antibiotics.